Next, you have to find the molar mass of Ca (40.08 g/mol) and Cl (35.45 g/mol). From the chemical formula that I provided, we can see that there are 2 atoms of chlorine and the molar mass of 35.45g/mol only accounts for one Cl atom. To account for both chlorine atoms, the molar mass has to be multiplied by 2: 2 × 35.45 g mol = 70.90 g/mol. The molecular mass is be a total sum atomic masses in the molecule So that the atomic mass of Ca is 40 The atomic mass of O is 16 The atomic mass of H is 1. There are two stable isotopes of calcium: Ca - 40 (39.96) and Ca - 46 (45.95). Using the average atomic mass of calcium from the periodic table, calculate the% abundance of each isotope of calcium. Model 2: Mass spectrometry Information: Mass Spectrometry is a powerful analytical tool used to determine the following information.
- Atomic Mass Of Carbon 12
- Atomic Mass Of Carbon
- Atomic Mass Of Cacl2
- Calcium Periodic Table
- Atomic Mass Of Cadmium
Atomic Mass Of Carbon 12
Please provide values below to convert Atomic mass unit [u] to kilogram [kg], or vice versa.
Atomic Mass Unit to Kilogram Conversion Table
Atomic Mass Of Carbon
| Atomic Mass Unit [u] | Kilogram [kg] |
|---|---|
| 0.01 u | 1.6605402E-29 kg |
| 0.1 u | 1.6605402E-28 kg |
| 1 u | 1.6605402E-27 kg |
| 2 u | 3.3210804E-27 kg |
| 3 u | 4.9816206E-27 kg |
| 5 u | 8.3027009999999E-27 kg |
| 10 u | 1.6605402E-26 kg |
| 20 u | 3.3210804E-26 kg |
| 50 u | 8.3027009999999E-26 kg |
| 100 u | 1.6605402E-25 kg |
| 1000 u | 1.6605402E-24 kg |
How to Convert Atomic Mass Unit to Kilogram
1 u = 1.6605402E-27 kg
1 kg = 6.0221366516752E+26 u
Example: convert 15 u to kg:
15 u = 15 × 1.6605402E-27 kg = 2.4908103E-26 kg
Popular Weight And Mass Unit Conversions
Convert Atomic Mass Unit to Other Weight and Mass Units
Mole
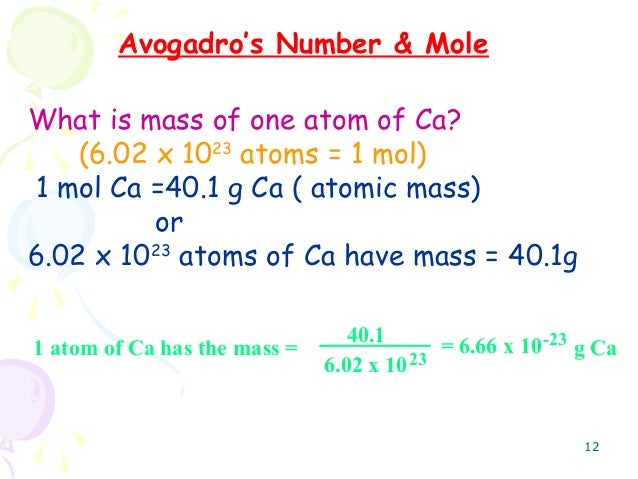
All substances consist of atoms or molecules. In chemistry, it is important to measure their amounts accurately. The mole is used to express the amounts of reactants and products of chemical reactions. The mole, symbol mol, is the SI unit of amount of substance. One mole contains exactly 6.02214076×10²³ elementary entities. This number is the fixed numerical value of the Avogadro constant, NA, when expressed in the unit mol⁻¹ and is called the Avogadro number. The amount of substance, symbol n, of a system is a measure of the number of specified elementary entities. An elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an electron, any other particle or specified group of particles.
Avogadro constant NA = 6.02214076×10²³ mol⁻¹

In other words, the mole is the amount of substance equal in mass to the combined mass in atomic mass units of the atoms of molecules of the substance multiplied by the Avogadro constant or Avogadro number. The mole as the unit of measurement for amount of substance is one of the seven base units of the International System of Units (SI). Its symbol is mol. One mole of pure carbon-12 has a mass of exactly 12 grams.
Molar mass
The molar mass is a physical property, which is defined as the mass of a substance divided by its amount of substance in moles. In other words, it is the mass of one mole of a particular substance. In SI, the unit for molar mass is kg/mol. However chemists almost always express molar masses in g/mol for convenience.
Molar mass = grams/mole
Molar Masses of Elements and Compounds
Compounds are substances consisting of several different atoms held together by chemical bonds. For example, the following substances that can be found in every kitchen are compounds:
- salt (sodium chloride) NaCl
- sugar (sucrose) C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁
- vinegar (acetic acid solution) CH₃COOH
The molar mass of elements in grams per mole is numerically equal to their atomic mass in unified atomic mass units (u) or daltons (Da). The molar mass of compounds is equal to the sum of molar masses of the atoms which form the compound. For example, the molar mass of water (H₂O) is approximately 1 × 2 + 16 = 18 g/mol.
Molecular Mass
Molecular mass (older name molecular weight) is the mass of a molecule calculated as the sum of the mass of each atom in the molecule multiplied by the number of atoms of that element in the molecule. Molecular mass is a dimensionless quantity numerically equal to the molar mass. Though molecular and atomic mass values are dimensionless, they are given the unit dalton (Da) or unified atomic mass unit (u), which is approximately the mass of a single proton or neutron and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.
Calculating the Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is calculated using three steps:
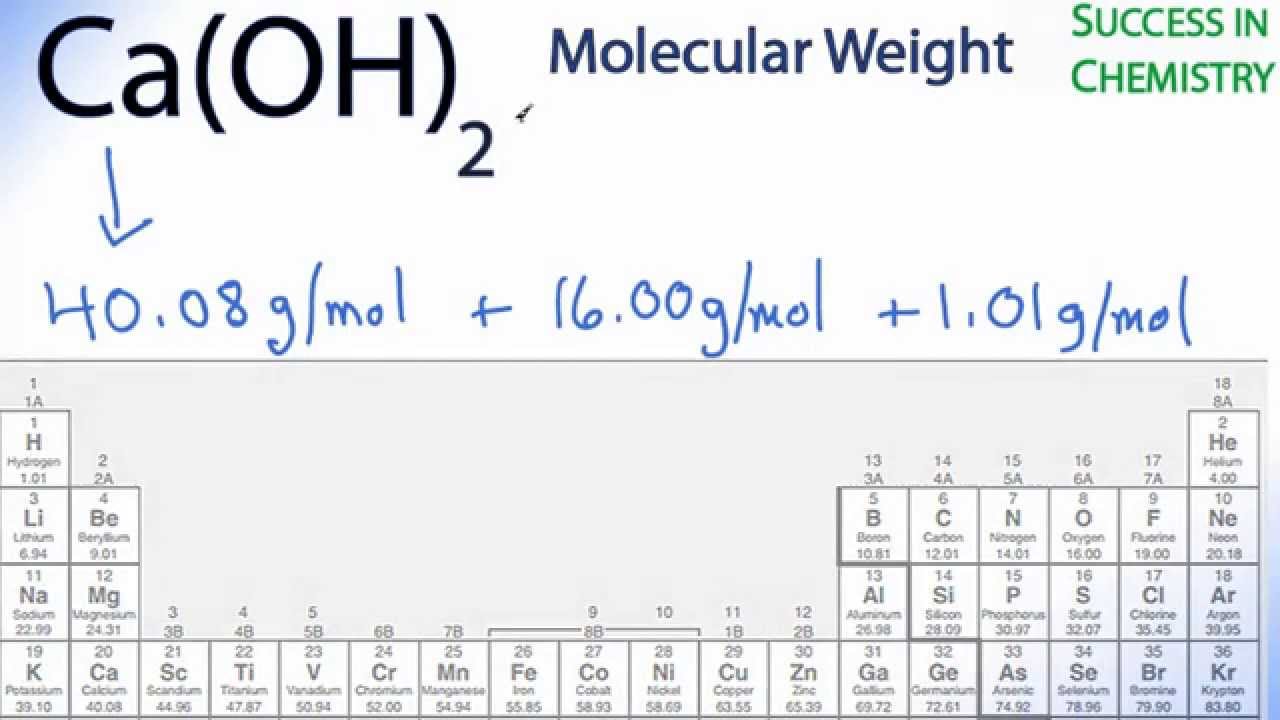
- Finding the atomic masses of elements in the periodic table.
- Counting the number of atoms of each element in the compound.
- Finding the molar mass by means of calculating the sum of the atomic weight of the atoms, which form the compound multiplied by the their numbers.
For example let us calculate the molar mass of the acetic acid
It contains:
- 2 atoms of carbon
- 4 atoms of hydrogen
- 2 atoms of oxygen
Atomic Mass Of Cacl2
Now, the calculation:
- Carbon C = 2 × 12.0107 g/mol = 24.0214 g/mol
- Hydrogen H = 4 × 1.00794 g/mol = 4.03176 g/mol
- Oxygen O = 2 × 15.9994 g/mol = 31.9988 g/mol
- Molar mass = 24.0214 + 4.03176 + 31.9988 = 60.05196 g/mol
Calcium Periodic Table

Atomic Mass Of Cadmium
Our calculator does the same calculation. You can enter the formula and check.
